Model by Prof. Dr. Javeria, Karachi
J. Shaikh. Bilal Alvi, S.Munawar, Department of Architecture and Built Environment..
Abstract: The healthcare industry is becoming a model for the larger world in developing an ecological environment; medicine approach is: “first do no harm”. Developing new hospital campus in urban site; ideas of therapeutic architecture based on ASHRAE recommendations of sustainable site planning principles. For the energy and environmentally efficient architectural model for the design of Lyari hospital, we developed a series of models using native and adopted architectural strategies. The environmentally efficient master plan will form design decisions so that the footprint of the proposed development does not overwhelm the capacity of the site from HVAC standpoint.
The climate of Karachi has additional challenge of humidity control, compared to rest of the cities in Pakistan due to the proximity of sea. For all code and standards defined in climate consultant, the comfort zone of winter and summer temperature range lies between 20oC and 31oC respectively. The traditional passive architectural strategies are still most popular in designing the climatic responsive buildings for Karachi. The Double skin façade building presented a model of the envelop for Karachi which was simulated to be 87% more efficient from HVAC perspective
Keywords: Healthcare care energy efficiency and climate consultant
INTRODUCTION
Establishing sustainable goals: early in the process, evaluate site under consideration for environmental opportunities and constrains. Development of an environmental management masters plan during the first phase of site development to ensure the preservation of the site’s ecologically significant areas. The above shown environmentally management master plan will inform design decisions so that the foot print of the proposed development does not over whelm the capacity of the site. The project is at Lyari, where the technology of indoor environmental comfort goals to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design fosters healing environment in this specific research.
The other issue is to document the specific conditions of hospital buildings in terms of its design determinants, spatial organization and areal distribution as there is very little unpublished information available in Pakistan concerning energy aspects of hospital buildings e.g. Lyari.
BACKGROUND
The objectives of the Project are to improve the quality of life and the accessibility to health services of the regional people in Sindh by establishing a specialized children’s hospital in Lyari.
- a) To function as a tertiary hospital to cure the diseases of children including infants in Karachi
- b) To increase the health care coverage of children patients in Northern Sindh.
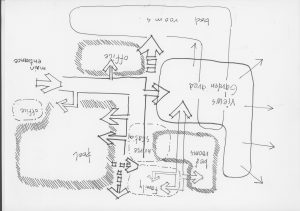
The site is located at cheel chawk, it is designed for an NGO, with human comfort as primary object, in developing new hospital campuses on urban sites., ideas of therapeutic landscape merge with sustainable site-planning principles in developing healing gardens, green roofs, and native plantings.
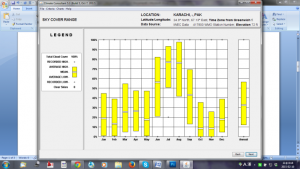
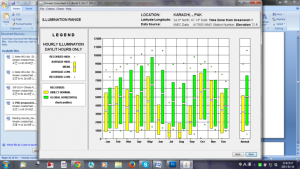
The climate consultant software 2) defines the criteria for each comfort model, using its specific details for 14 design strategies. This selection further figures out the percentage of comfort range in psychometrics chart.
| Plan and sectional schematics development | Climate Consultant air and radiation |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
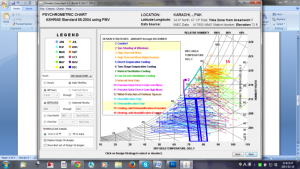 |
Fig.1 analysis of the design
The sun shading, thermal mass and ventilation requirements are important passive cooling strategies weather file of Karachi city in Pakistan[1]. The access to data maps and drawings concerning hospital buildings is a major constraint in Pakistan. The overall structure and nature of maintenance and management system of hospital buildings is still at its infancy level.
The variety of analysing climatic parameters for a particular location is facilitated with the help of available human thermal comfort models (HTCMs). Each model set particular criteria based on the descriptive study of a specific code and standard. The simplified explanation of each HTCM[2] is prescribed before the selection. This paper gives a comparative analysis for the application of various HTCMs using a
TABLE. 1 HEALTH SERVICES AND AFFAIRS
[1] Climate Consultant Graphic Based Computer Program: Climate Consultant 6.0 BETA (built 3) November 11, 2014 (http://www.energy-design-tools.aud.ucla.edu/climate-consultant/request-climate-consultant.php
[2] Energy Design Tool: (http://www.energy-design-tools.aud.ucla.edu/)
| Classification | 2016-2017 | 2017-2018 |
| Medical appliances equipments and product | 260 | 100 |
| Hospital services | 8180 | 8306 |
| Public service: health | 1029 | 356 |
| Administration of Health | 394 | 1255 |
| Total | 9863 | 10017 |
Hospital management team faces impossible choices to balance cost and quality of care.
- LITERATURE REVIEW
A setting designed to use natural capital- sun, wind and water to reduce operating costs and maintenance; uses renewable resources Malkin, J. (1992).
The general Hospital site in Lyari, SPO (strengthening Participatory Organization): In developing new hospital campus in urban site ideas of therapeutic landscape merge with sustainable site planning principles in developing healing gardens, green roofs, and native planting Stichler, J. F. (2008). For the landscape design of Lyari hospital, we developed a series of gardens using native and adopted planting strategies, permeable paving, water features in the campus forecourt, and an intimate healing garden on a rooftop nestled between inpatient wings Hannen, Scott. (2009).
- MATERIALS AND METHODS
The main reason it that, in Karachi, there is little existing research on EBD, or even POE (post occupancy evaluation) from HVAC perspective of existing hospitals, which is the most basic material for EBD research. Though we as researcher planned to design based on resources and available research.
Lyari Hospital is a 300-bed hospital designed in 2013, this project is a new expansion of 300 bed hospital next to the existing hospital making it is total of 600 bed general hospital and the biggest acute bed hospital in the region.
- DISCUSSION
The living building site is based on responsible site selection, limits to growth, habitat exchange, here following the green guide. Healthcare has deep roots and successes in both the policy and implementation arenas associated with toxic and waste reduction, ecological footprint responding to the layered ecological urges of our time. To have less load on HVAC.
In healthcare, sustainable building represents a bold move towards precaution and prevention. The building stands for health.
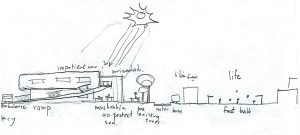
1.2. Climate Consultant Methods and Scopes
Key building performance strategy Site
Mold free environment safeguard sensitive patients [1]
Green roof
Energy
Double skin façade [2]
Metal elements avoided in room for electromagnetically sensitive patient: electronic equipment housed elsewhere, and metal –free furniture used where possible[3]
Wood floors instead of carpet in all areas, to reduce HVAC load.
Hard materials preferred to soft ones to eliminate off gassing [4]
The aim is if the healthcare industry become a model for the larger world in developing an ecological approach to these environmental and health challenges? [5]Central to these approaches to medicine is the axiom: “first do no harm” Ausubel, K. (2004).
ASHRAE standard 55 and current handbook of comfort model (option 2)
ASHRAE handbook of fundamental comfort model up through 2005 (option 3)
Adaptive comfort model in ASHRAE standards 55-2010 (option 4)
For the purpose of sizing residential heating and cooling systems, the indoor dry bulb design conditions should be between 68°F (20°C) to 75°F (23.9°C)
80% relative humidity and 66°F (18.9°C) wet bulb is used as the upper limit and 27°F (-2.8°C) dew point is used as the lower limit.
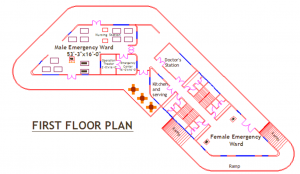
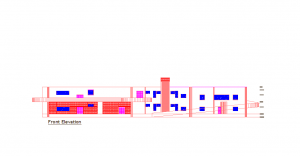
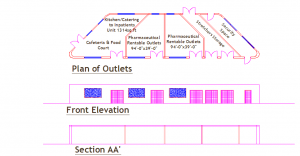
The plan of the hospital
The climate responsive building can be an effective cost efficient strategy for the residential building sector requiring an in depth analysis of Karachi’s climate. The better understanding of temperature, Mutangadura, G. B. (2004). humidity conditions and various other climatic elements can help in designing energy efficient buildings. The performance, comfort and energy use in residential buildings is influenced by the climatic conditions and the way in which a particular residence responds and develops the local micro- climate[1]. The reduced need for the air conditioners and HVAC load in healthcare sector can also effectively minimize the CO2 emissions specifically.
2.2. Envelope design
The architectural elements like wall, roof and window must have a required minimum level of thermal resistance. It can be made possible with the use of locally available insulating materials, increased thickness, and double glazed pan windows, suggested in redesigning the HVAC systems.
- a) Site survey for the target area for the medical treatment of the hospital including existing hospitals;
- b) Analysis of the requirement for the project including the function of the hospital, medical plan, layout plan, operating and maintenance plan, and so on;
- c) Finalizing the medical plan in accordance with the function of the hospital
Site 300x 400 feet
- 30 % circulation + 200’x200’ diagnosis
- 10 % site for spine circulation
- 300 bed 200’x200’ + 30% circulation
- Emergency 100’x100’+ 50% circulation
- Outpatient unit 100’x200’+ 50% circulation
Thus air quality up gradation, increased day lighting, high-performance ceiling, work path planning and support distribution, communication system, standardized, non handed rooms, single, acuity, adoptable rooms.
Perhaps the bottom line on the health and human performance benefits of green building comes to this
- a) If we know from personal and anecdotal experience that having a thermally comfortable, well lit, properly ventilated work space, preferably with daylight and a view of nature, is likely to have a positive effect on our well-being and morale, and therefore would inspire greater work performance; and
- b) If sustainable physical elements, such as adequate air exchange produce any positive in employee and health and well-being; and lower the need of HVAC systems and facilitating the HVAC services.
- CONCLUSION
The design posed two fundamental questions
- What specific innovations could be made to improve healthcare delivery- and at what cost on HVAC.
The design innovations and their costs were organized into four categories
- Energy and Environment
- Indoor environmental quality (IEQ) for HVAC
- Operational efficiency
- Infection Control
- Building operation for reduced energy consumption and lowering the requirements for HVAC: includes in terms of energy and environment primarily sustainable systems- energy, water, secondly, sustainable system management, and tertiary automatic controlled operable windows for ventilation.
- Rooftop HVAC unit with view of fresh air intake vent, improved for the burns department. Ventilation duct with outlet diffuser vent. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort is simulated for Lyari hospital. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality better from 75%.
- HVAC is an important part of healthcare structures such as hospitals environments, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fresh air from outdoors. Thus thus design is proposed based on ASHRAE’s recommendation for human comfort.
- Ventilating air in any space to provide high indoor air quality which involves temperature control, oxygen replenishment, and removal of moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, carbon dioxide, and other gases. Ventilation removes unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduces outside air, keeps interior building air circulating, and prevents stagnation of the interior air. This is achieved for 90% from the ribbon balcony wrapping around the entire building.
The Enercon in 1994 worked with a team of Oxford Brooks University, UK for setting appropriate indoor temperature standards for Pakistan.